With the amount of configuration involved in a typical L3VPN configuration, troubleshooting process can get pretty chaotic, especially in a time-constrained environments like CCIE lab. That’s why it is extremely important to have a well-structured approach to quickly narrow down the potential problem area. I used the below algorithm while preparing for my lab exam. Like most of the networking problems, troubleshooting of L3VPNs can and must be split into two different phases - control plane and data plane. All steps must be done sequentially with each next step relying on the successful verification of all previous steps.
- Problem definition
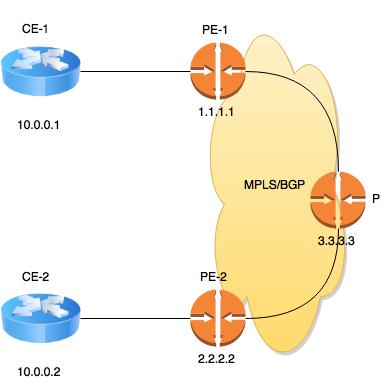
- CE-1 (10.0.0.1) can not reach CE-2 (10.0.0.2)
Troubleshooting of L3VPN control plane
- Check if PE-2 can reach CE-2 from it’s VRF
ping vrf A 10.0.0.2. If not - make sure the PE-CE routing protocol is configured to propagate CE subnet. - Make sure that 10.0.0.2 is in vpnv4 BGP RIB on PE-2 with
show bgp vpnv4 unicast 10.0.0.2/32. If not - make sure this route gets redistributed into vpnv4 bgpaddress family ipv4 vrf A. - Check vpnv4 BGP peerings on PE-2 with
show ip bgp vpnv4 unicast all summary. In our case it peers with VPNV4 Route-Reflector (3.3.3.3). If not - check that the neighbor is configured and activated underaddress family vpnv4and that the neighbor address (3.3.3.3) is reachable. - On intermediate Route-Reflector P check that the CE-2 subnet is present in BGP RIB with
show ip bgp vpnv4 unicast 10.0.0.2/32. If not - check that PE-02 advertises this subnet to P withshow ip bgp vpnv4 unicast all neighbor 3.3.3.3 advertised - On PE-1 check that CE-2 subnet is present in vpnv4 BGP RIB with
show ip bgp vpnv4 unicast 10.0.0.2/32. If not - make sure P is one of it’s vpnv4 peers and that P advertises this subnet to PE-1 - Check that vrf A on PE-1 contains the advertised subnet 10.0.0.2 with
show ip route vrf A 10.0.0.2. If not - make sure that import route target on PE-1 equals to export route target on PE-2 and that this subnet is redistributed from BGP into PE-CE routing protocol
Troubleshooting of L3VPN data plane
If control plane is working fine, next step is to troubleshoot the data plane. This can be most difficult since LDP can be so easily broken by summarisation or filtering. However, in general, data plane troubleshooting will consist of the following steps:
- Make sure PE-2 knows how to reach PE-1 over the LSP with
show mpls forwarding 1.1.1.1. - Make sure PE-1 knows how to reach PE-2 over the LSP with
show mpls forwarding 2.2.2.2. - MPLS-trace the path from PE-2 to PE-1 with
traceroute mpls ipv4 1.1.1.1 source 2.2.2.2. - Do the same in the other direction. In case traceroute stops, jump on the last responded node and check that LDP peering
is running with all its neighbors with
show mpls ldp neighbor